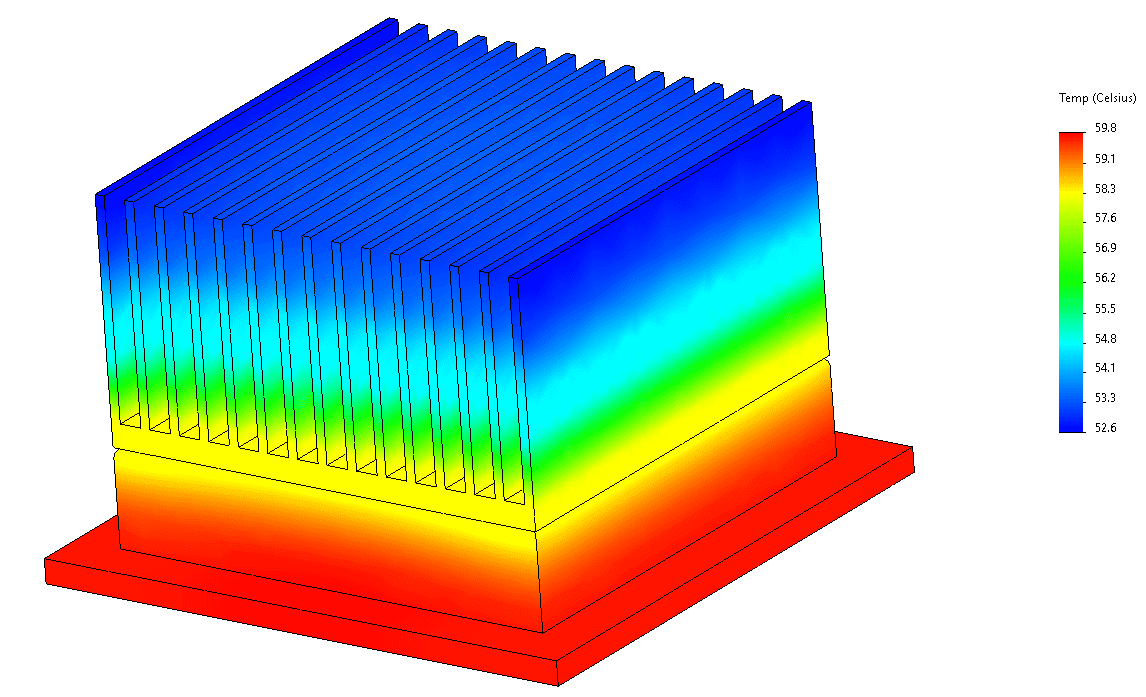
Thermal management is a critical aspect of modern engineering, ensuring that electronic devices, industrial machinery, and energy systems operate efficiently and reliably. As technological advancements push the boundaries of performance, the demand for effective cooling solutions has grown significantly. Without proper thermal management, excessive heat can lead to reduced efficiency, component degradation, and system failures.
Key Components and Methods in Thermal Management Systems
Effective thermal management involves a combination of passive and active cooling techniques. The primary methods include:
- Heat Sinks: These passive components dissipate heat by increasing the surface area exposed to the surrounding air.
- Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs): Materials such as thermal pastes, pads, and phase change materials improve heat transfer between surfaces.
- Liquid Cooling Systems: Advanced systems use coolants to absorb and transfer heat away from sensitive components.
- Phase Change Cooling: Materials that undergo phase transitions, such as vapor chambers, efficiently transfer heat.
- Thermoelectric Cooling: Semiconductor-based devices use electric current to transfer heat, providing precise temperature control.
Each of these methods plays a vital role in optimizing thermal performance and extending the lifespan of electronic and mechanical systems.
The Role of Thermal Analysis in Optimizing Cooling Solutions
Thermal analysis is an essential process in designing and evaluating cooling solutions. Engineers utilize various simulation and testing techniques to predict heat distribution, assess component efficiency, and optimize cooling strategies. The most common thermal analysis techniques include:
- Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD): A simulation-based approach that models heat flow and temperature distribution.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): Used to evaluate the thermal stress and heat transfer characteristics of materials.
- Infrared Thermography: A non-contact method for visualizing temperature variations in real-time.
- Thermal Conductivity Testing: Measures the ability of materials to conduct heat effectively.
By leveraging thermal analysis, designers can enhance system reliability, reduce energy consumption, and minimize overheating risks.
Advanced Technologies Driving Innovations in Thermal Management
The rapid advancement of technology has led to the development of innovative cooling solutions. Some of the latest trends include:
- Nanotechnology-Based Cooling Materials: Nanofluids and nano-coatings offer superior thermal conductivity and heat dissipation.
- AI-Driven Thermal Management: Artificial intelligence and machine learning optimize cooling strategies in real-time.
- 3D-Printed Heat Sinks: Additive manufacturing enables custom heat sink designs with improved thermal efficiency.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): These materials store and release heat, improving thermal regulation in electronics and energy systems.
These cutting-edge solutions are transforming the way industries manage heat, enhancing performance across various sectors.
Conclusion: The Future of Thermal Management and Its Growing Significance
As electronic devices and industrial systems continue to evolve, the need for advanced thermal management solutions remains crucial. Efficient cooling strategies not only improve performance and longevity but also contribute to energy savings and environmental sustainability. With ongoing research and technological advancements, the future of thermal management promises even more innovative and effective solutions to meet the growing demands of modern applications.